1. Models & Layers
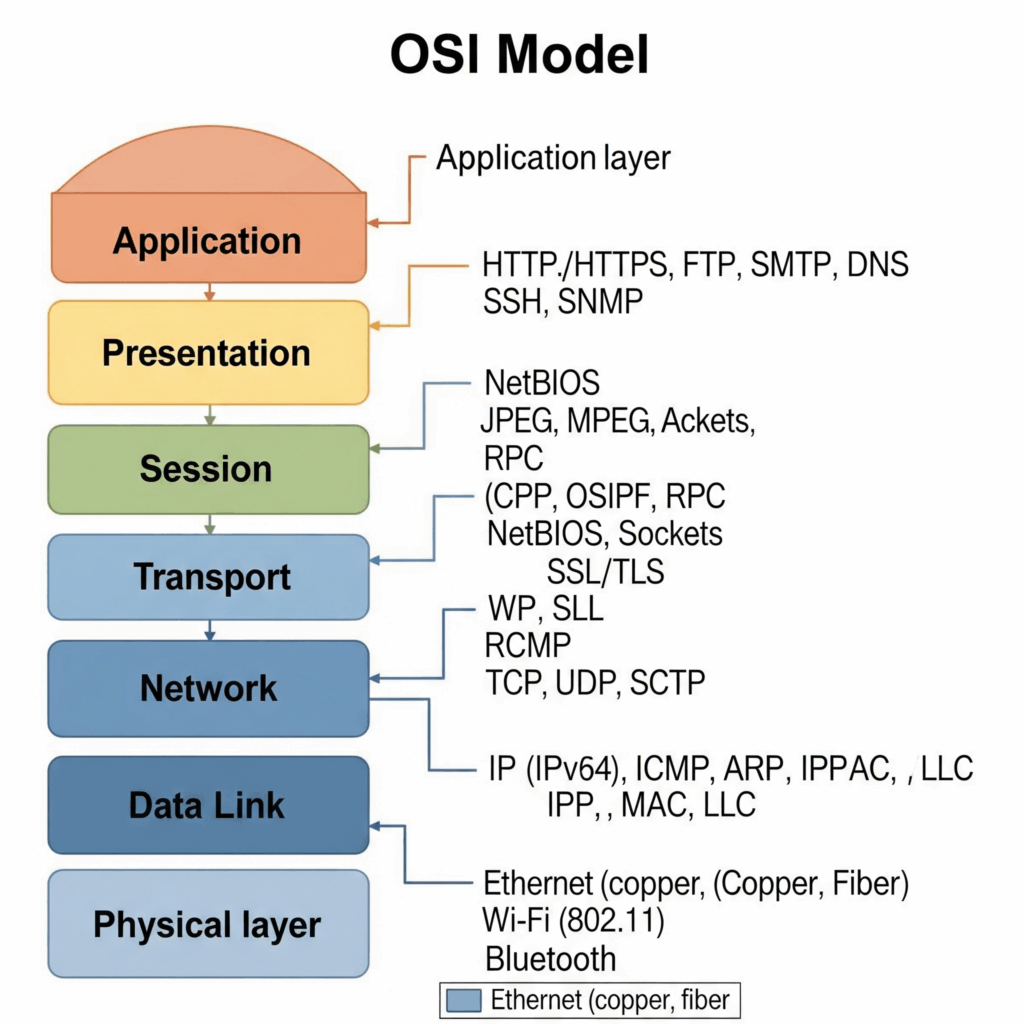
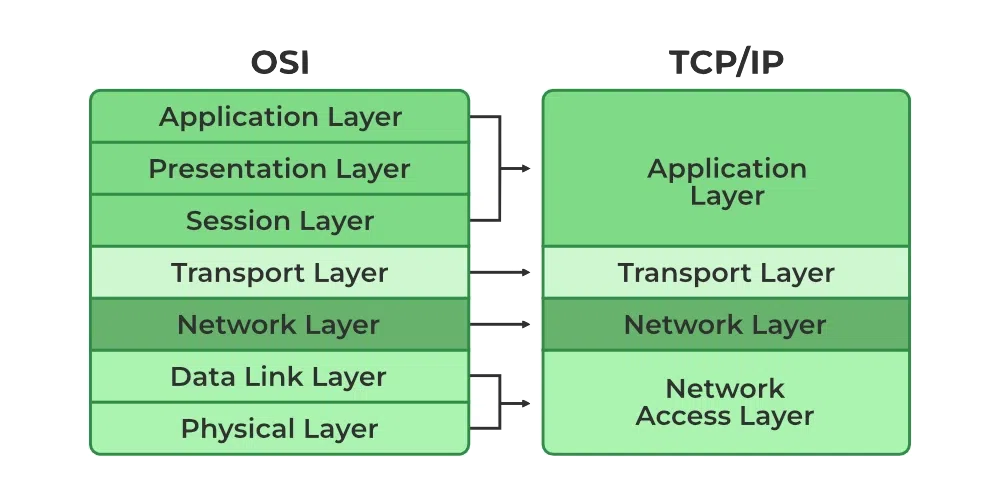
- OSI Model (7 layers → APSTNDP)
👉 Application → Presentation → Session → Transport → Network → Data Link → Physical - TCP/IP Model (4 layers → ATIN)
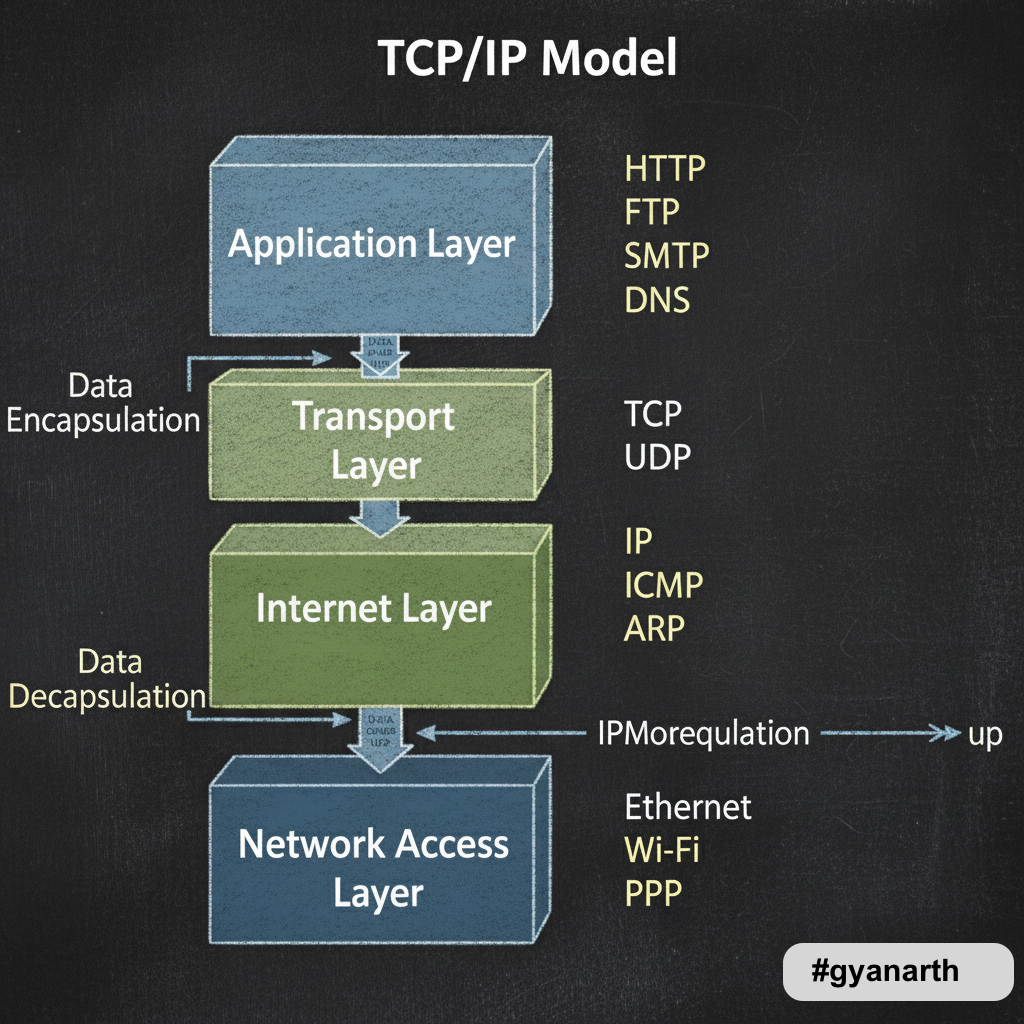
👉 Application → Transport → Internet → Network Access
2. Layers & Functions (with protocols)
🔹 Application Layer (OSI & TCP/IP)
- Role: User interaction, data generation, services.
- Protocols: HTTP/HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, POP3, IMAP, DNS, SNMP.
🔹 Presentation Layer (OSI)
- Role: Data formatting, encryption, compression.
- Analogy: Unboxing pizza.
🔹 Session Layer (OSI)
- Role: Start, manage, end communication.
- Analogy: Conversation with delivery agent.
🔹 Transport Layer (OSI & TCP/IP)
- Role: Reliable delivery, segmentation, flow control.
- Protocols: TCP (reliable), UDP (fast).
- Ports: HTTP 80, HTTPS 443, etc.
- Analogy: Pizza box (safe delivery).
🔹 Network Layer (OSI) / Internet Layer (TCP/IP)
- Role: Logical addressing, routing.
- Protocols: IP (IPv4, IPv6), ICMP, ARP, RARP, IGMP.
- Analogy: GPS for best route.
🔹 Data Link Layer (OSI) / Network Access (TCP/IP)
- Role: Framing, MAC addressing, error handling.
- Protocols: Ethernet, PPP, Frame Relay, HDLC.
- Analogy: Traffic rules.
🔹 Physical Layer (OSI)
- Role: Raw bits, cables, hubs, signals.
- Analogy: Roads for delivery.
3. Common Protocols & Ports (must memorize 🚨)
| Protocol | Port |
|---|---|
| FTP | 20, 21 |
| SSH | 22 |
| Telnet | 23 |
| SMTP | 25 |
| DNS | 53 |
| HTTP | 80 |
| HTTPS | 443 |
| SNMP | 161 |
| DHCP | 67, 68 |
4. Quick Pizza Story (Mnemonic)
| Layer | Mnemonic | Function | Pizza Analogy 🍕 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | Please | Raw data bits | Roads for delivery |
| Data Link | Do | Framing, MAC | Traffic rules |
| Network | Not | IP, routing | GPS for route |
| Transport | Throw | TCP/UDP | Pizza box (safe) |
| Session | Sizzler | Manage sessions | Talk to agent |
| Presentation | Pizza | Format, encrypt | Nicely arranged toppings |
| Application | Away | User interaction | Eating the pizza |
✅ Tips for Exam:
- Always match protocols to layers (very common Q).
- Remember APSTNDP & ATIN mnemonics.
- Learn well-known ports (20–25, 53, 80, 443, 161, 67/68).
- Use pizza analogy to recall functions quickly.
MCQ
Which layer of the OSI model is responsible for logical addressing and routing of packets?
a) Data Link
b) Transport
c) Network
d) Application
Answer: c) Network
2. Which of the following is NOT a function of the Transport Layer?
a) Error detection and correction
b) Port addressing
c) Flow control
d) IP addressing
Answer: d) IP addressing
3. In the OSI model, which layer establishes, manages, and terminates communication sessions?
a) Presentation
b) Transport
c) Session
d) Data Link
Answer: c) Session
4. Which protocol operates at the Application Layer of the OSI model?
a) TCP
b) FTP
c) ICMP
d) ARP
Answer: b) FTP
5. Which layer is responsible for translating data between the application layer and the network format?
a) Presentation
b) Session
c) Transport
d) Physical
Answer: a) Presentation
6. What is the primary responsibility of the Data Link Layer in the OSI model?
a) Logical addressing and routing
b) Frame synchronization and error detection
c) Bit-level transmission of data
d) Encryption and decryption
Answer: b) Frame synchronization and error detection
7. Which port number is used by the HTTP protocol?
a) 25
b) 53
c) 80
d) 443
Answer: c) 80
8. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used to resolve:
a) IP addresses to MAC addresses
b) Domain names to IP addresses
c) Port numbers to services
d) MAC addresses to IP addresses
Answer: a) IP addresses to MAC addresses
9. Which layer of the TCP/IP model combines the functionality of the OSI Data Link and Physical layers?
a) Application
b) Network Access
c) Internet
d) Transport
Answer: b) Network Access
10. Which layer of the OSI model handles the conversion of bits to electrical signals?
a) Data Link
b) Physical
c) Network
d) Transport
Answer: b) Physical
11. Which protocol is responsible for email retrieval?
a) SMTP
b) POP3
c) SNMP
d) ICMP
Answer: b) POP3 downloads emails from an email server to a device over a TCP/IP connection. It only downloads emails from the inbox folder, and it deletes the emails from the server after downloading.
12. Which layer is responsible for segmentation and reassembly of data?
a) Application
b) Transport
c) Network
d) Data Link
Answer: b) Transport
13. Which protocol is used for secure communication over a computer network?
a) HTTP
b) UDP
c) HTTPS
d) FTP
Answer: c) HTTPS
14. What is the primary function of ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)?
a) Routing data packets
b) Error reporting and diagnostics
c) Establishing end-to-end communication
d) Resolving domain names
Answer: b) is used for reporting errors and performing network diagnostics. In the error reporting process, ICMP sends messages from the receiver to the sender when data does not come though as it should.
15. What is the purpose of the DNS protocol?
a) Translate domain names to IP addresses
b) Resolve IP to MAC addresses
c) Provide secure file transfer
d) Manage remote logins
Answer: a) Translate domain names to IP addresses
16. Which layer is responsible for data encryption and compression?
a) Application
b) Presentation
c) Transport
d) Session
Answer: b) Presentation
17. Which of the following is a connectionless protocol?
a) TCP
b) HTTP
c) UDP
d) FTP
Answer: c) UDP
18. What is the maximum size of an IPv4 address?
a) 32 bits
b) 64 bits
c) 128 bits
d) 256 bits
Answer: a) 32 bits
19. Which of the following protocols is used to monitor and manage network devices?
a) FTP
b) SNMP
c) SMTP
d) DHCP
Answer: b) SNMP
20. What is the function of the DHCP protocol?
a) Translate domain names to IP addresses
b) Dynamically assign IP addresses
c) Encrypt transmitted data
d) Provide routing paths for packets
Answer: b) Dynamically assign IP addresses
