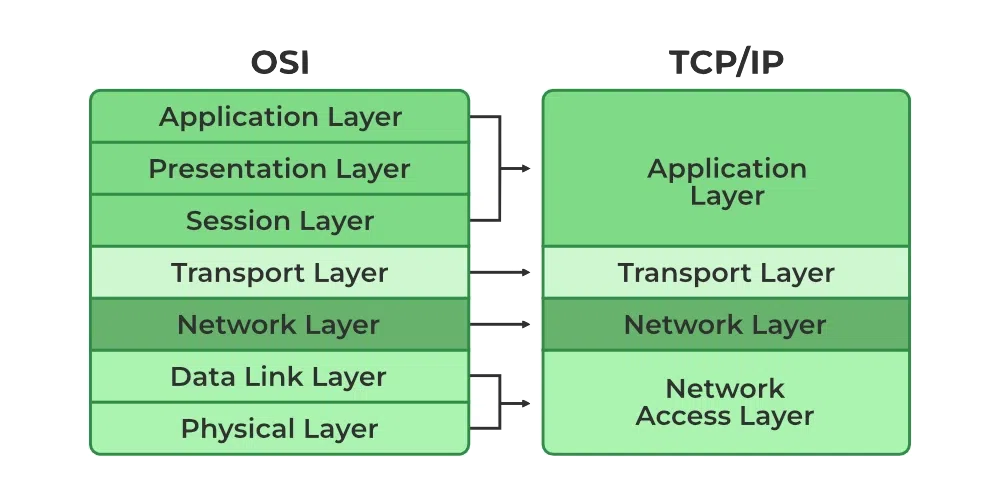
Difference between osi and tcp ip model:
| Feature | OSI Model | TCP/IP Model |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Layers | 7 | 4 |
| Purpose | Theoretical, for understanding networks. | By ISO to standardise communication systems. |
| Development | By ISO to standardize communication systems. | By DARPA to connect military and academic networks. |
| Protocol Dependency | Protocol-independent, abstract functionality. | Protocol-specific, integrates TCP, IP, HTTP, etc. |
| Modularity | Highly modular, easier to update. | Less modular, layers depend on each other. |
| Layer Functions | Separate Session and Presentation layers. | No separate Session/Presentation layers (handled in Application). |
| Addressing | Uses logical (IP) and physical (MAC) addressing. | Uses real-world IP addresses and port numbers. |
| Examples | Ethernet, ATM (conceptual examples). | HTTP, FTP, SMTP, TCP, IP (real-world examples). |
| Approach | Top-down: Application to Physical. | Bottom-up: Network to Application. |
| Relevance | Teaching/reference model. | Used in actual internet technologies. |
Key Takeaways:
- OSI = Reference model, 7 layers, teaching-oriented.
- TCP/IP = Practical model, 4 layers, real-world networking.
Difference between OSI and TCP/IP models – MCQ
Basic Structure
- How many layers does the OSI model have?
a) 4
b) 5
c) 7
d) 8
Answer: c) 7 - Which of the following is a layer in the TCP/IP model but not in the OSI model?
a) Network Access
b) Presentation
c) Session
d) Physical
Answer: a) Network Access - Which OSI layer is responsible for translating and encrypting data?
a) Session Layer
b) Presentation Layer
c) Application Layer
d) Transport Layer
Answer: b) Presentation Layer - In the TCP/IP model, which layer corresponds to the OSI Application, Presentation, and Session layers?
a) Transport
b) Network
c) Application
d) Internet
Answer: c) Application - The TCP/IP model was developed by:
a) ISO
b) DARPA
c) IEEE
d) IETF
Answer: b) DARPA
Purpose and Development
- Which model is primarily used as a reference for understanding networks?
a) TCP/IP
b) OSI
c) Both
d) Neither
Answer: b) OSI - Why was the OSI model developed?
a) To implement internet technologies
b) To standardize communication systems
c) To replace TCP/IP
d) For hardware design
Answer: b) To standardize communication systems - What was the main objective behind the development of the TCP/IP model?
a) To create an abstract networking framework
b) To enable communication between military and academic systems
c) To ensure reliable hardware functionality
d) To design hardware protocols
Answer: b) To enable communication between military and academic systems
Protocol Dependency
- The OSI model is:
a) Protocol-dependent
b) Protocol-independent
c) Application-specific
d) Hardware-specific
Answer: b) Protocol-independent - Which model integrates specific protocols like TCP, IP, and UDP?
a) OSI
b) TCP/IP
c) Both
d) None
Answer: b) TCP/IP
Flexibility and Modularity
- Which model is more modular and allows easier updates?
a) OSI
b) TCP/IP
c) Both
d) None
Answer: a) OSI - In the TCP/IP model, changes to one layer may affect:
a) Only that layer
b) The entire stack
c) Only adjacent layers
d) None of the layers
Answer: b) The entire stack
Layer Functions
- Which of the following layers is NOT a part of the TCP/IP model?
a) Application Layer
b) Transport Layer
c) Session Layer
d) Internet Layer
Answer: c) Session Layer - Which OSI layer is responsible for maintaining connections and sessions?
a) Application Layer
b) Session Layer
c) Presentation Layer
d) Data Link Layer
Answer: b) Session Layer - The functions of the Presentation Layer in the OSI model are handled in the TCP/IP model by:
a) Transport Layer
b) Internet Layer
c) Application Layer
d) Data Link Layer
Answer: c) Application Layer
Addressing and Examples
- Which type of addressing is used by the OSI model?
a) Logical and Physical addressing
b) Only Logical addressing
c) Port numbers
d) Domain names
Answer: a) Logical and Physical addressing - In the TCP/IP model, addressing includes:
a) IP addresses and port numbers
b) Only MAC addresses
c) Only logical addresses
d) Only domain names
Answer: a) IP addresses and port numbers - Which of the following protocols belongs to the TCP/IP model?
a) Ethernet
b) ATM
c) HTTP
d) Token Ring
Answer: c) HTTP
Approach and Real-World Relevance
- The OSI model follows which approach?
a) Bottom-up
b) Top-down
c) Hybrid
d) None of the above
Answer: b) Top-down - Which model is widely implemented in the design of internet technologies?
a) OSI
b) TCP/IP
c) Both
d) None
Answer: b) TCP/IP - What is the primary use of the OSI model today?
a) Designing internet protocols
b) Teaching and as a reference model
c) Replacing TCP/IP
d) Developing real-world hardware
Answer: b) Teaching and as a reference model
