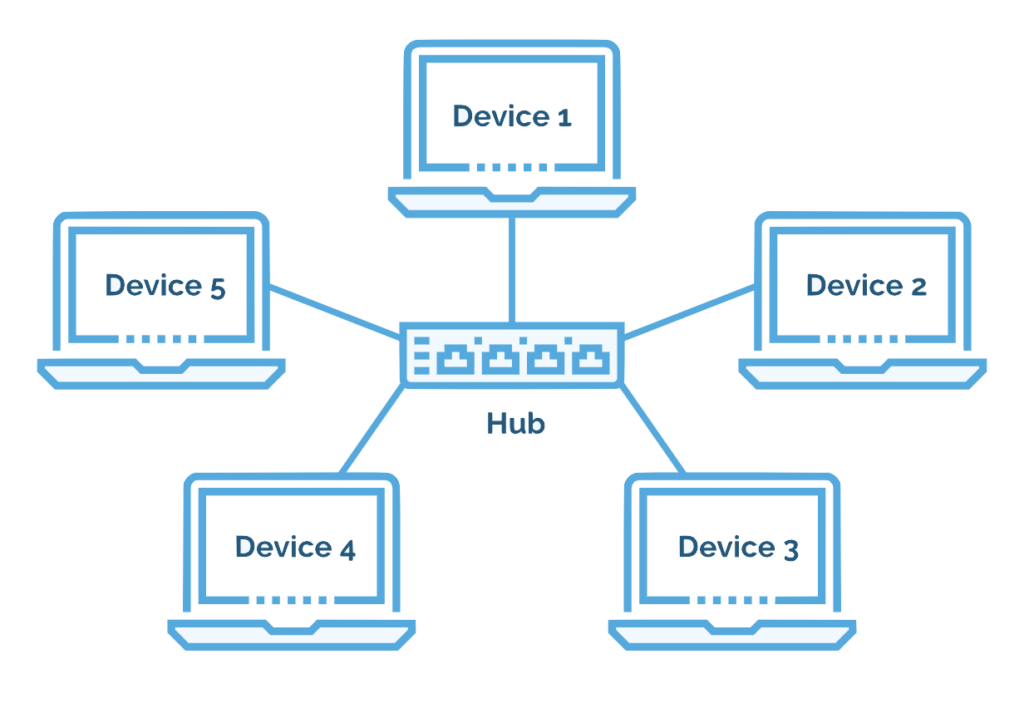
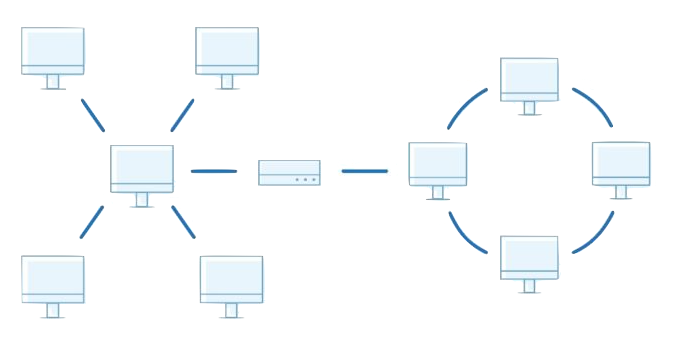
1. Star Topology
- Structure: Central node (hub or switch) connects all devices.
- Advantages:
- Easy to set up and manage.
- Fault isolation (failure in one device doesn’t affect others).
- Disadvantages:
- If the central hub fails, the entire network goes down.
- Requires more cables.
- Examples: Home or small office networks.
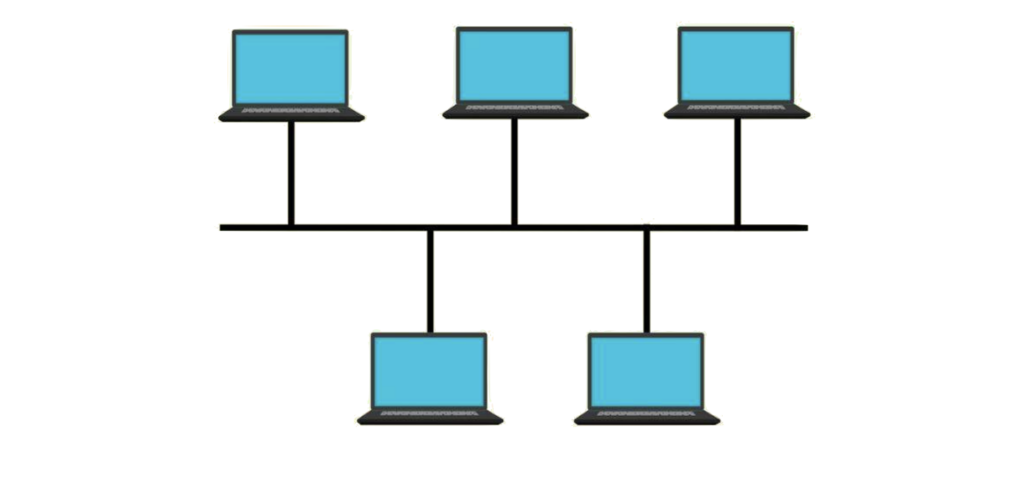
2. Bus Topology
- Structure: Single central cable (backbone) connects all devices.
- Advantages:
- Easy and cost-effective for small networks.
- Fewer cables required.
- Disadvantages:
- Collision of data can occur on the main cable.
- Difficult to troubleshoot.
- Failure of the backbone disrupts the entire network.
- Examples: Early LAN setups.
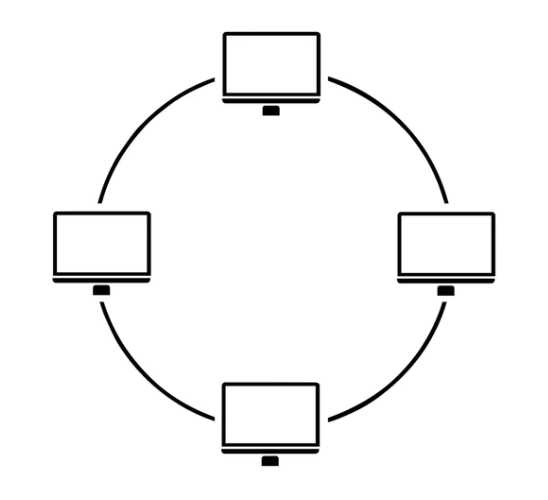
3. Ring Topology
- Structure: Devices are connected in a circular loop, with each device connected to two neighbours.
- Advantages:
- Equal access to resources (token-passing prevents collisions).
- Performs well under low traffic.
- Disadvantages:
- If one device fails, the entire network may fail (can be mitigated by dual rings).
- Adding/removing devices disrupts the network.
- Examples: Token Ring networks (obsolete now).
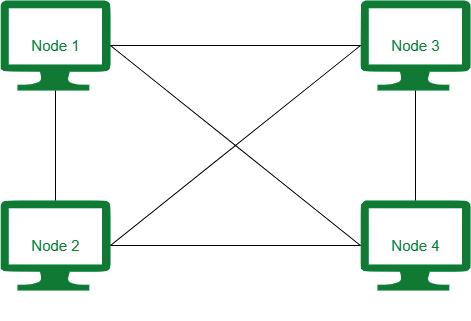
4. Mesh Topology
- Structure: Every device is connected to every other device.
- Advantages:
- High fault tolerance (multiple paths for data).
- Reliable and secure.
- Disadvantages:
- Expensive due to the large number of cables and ports.
- Complex setup and maintenance.
- Examples: WANs like the Internet.
5. Hybrid Topology
- Structure: Combines two or more topologies (e.g., star-bus, star-ring).
- Advantages:
- Flexible and scalable.
- Can leverage the strengths of individual topologies.
- Disadvantages:
- Complex design and higher costs.
- Examples: Large enterprise networks.
Key Comparison Table
| Topology | Fault Tolerance | Cost | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Star | Low (hub failure) | Moderate | Small office/home networks |
| Bus | None (backbone) | Low | Temporary setups, small networks |
| Ring | Moderate (token) | Moderate | Limited to legacy systems |
| Mesh | High | High | Large, secure, and reliable WANs |
| Hybrid | Depends on mix | High | Scalable enterprise networks |
🚀 TOP 55 IMPORTANT MCQs ON NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
⭐ SECTION 1 — BASIC TOPOLOGIES
1. Which topology has a central controller or hub?
A. Bus
B. Star
C. Ring
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: B
2. Which topology is MOST widely used in LANs today?
A. Bus
B. Mesh
C. Star
D. Ring
✔ Ans: C
3. In which topology do all computers share a single communication line?
A. Bus
B. Star
C. Tree
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: A
4. Failure of a single node affects the entire network most severely in:
A. Mesh
B. Star
C. Bus
D. Ring
✔ Ans: C
5. Which topology uses a token for communication?
A. Mesh
B. Ring
C. Bus
D. Hybrid
✔ Ans: B
6. In a fully connected mesh topology, number of links required for n devices =
A. n(n – 1)
B. n – 1
C. n/2
D. n(n – 1)/2
✔ Ans: D
7. Topology resistant to node failure (high reliability):
A. Ring
B. Bus
C. Mesh
D. Star
✔ Ans: C
8. Which topology is used in telephone networks?
A. Ring
B. Star
C. Bus
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: B
9. Which topology is most secure?
A. Mesh
B. Bus
C. Ring
D. Star
✔ Ans: A
10. Which topology is least expensive to install?
A. Bus
B. Star
C. Ring
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: A
⭐ SECTION 2 — FAILURES & PERFORMANCE
11. If the central hub fails, the entire network fails in which topology?
A. Bus
B. Mesh
C. Ring
D. Star
✔ Ans: D
12. Cable failure affects the entire network in:
A. Star
B. Bus
C. Mesh
D. Hybrid
✔ Ans: B
13. Message always travels in one direction in:
A. Bus
B. Ring
C. Star
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: B
14. Which topology has the highest redundancy?
A. Ring
B. Mesh
C. Star
D. Bus
✔ Ans: B
15. Which topology is MOST difficult to install and maintain?
A. Bus
B. Star
C. Ring
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: D
⭐ SECTION 3 — ADVANCED TOPOLOGIES
16. Tree topology is a combination of:
A. Star + Mesh
B. Bus + Star
C. Ring + Star
D. Bus + Mesh
✔ Ans: B
17. A topology combining two or more topologies is called:
A. Ring
B. Hybrid
C. Mesh
D. Tree
✔ Ans: B
18. Which topology is hierarchical in structure?
A. Bus
B. Ring
C. Tree
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: C
19. Which topology is used in corporate networks and universities?
A. Bus
B. Tree
C. Ring
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: B
20. Hybrid topology is used in:
A. WANs
B. Ethernet LANs
C. Small home networks only
D. Token Ring networks
✔ Ans: A
⭐ SECTION 4 — PROTOCOLS & TOPOLOGIES
21. Token Ring uses which topology?
A. Mesh
B. Physical star, logical ring
C. Only ring
D. Star only
✔ Ans: B
22. Ethernet originally used which topology?
A. Star
B. Ring
C. Mesh
D. Bus
✔ Ans: D
23. Modern Ethernet uses:
A. Ring
B. Bus
C. Star
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: C
24. FDDI uses which topology?
A. Bus
B. Dual Ring
C. Mesh
D. Star
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 5 — DISTANCE, SCALABILITY, EFFICIENCY
25. Which topology is best for long-distance communication?
A. Bus
B. Ring
C. Star
D. Tree
✔ Ans: D
26. Which topology is most scalable?
A. Star
B. Mesh
C. Tree
D. Bus
✔ Ans: C
27. Adding new nodes is simplest in:
A. Mesh
B. Bus
C. Star
D. Ring
✔ Ans: C
28. Which topology suffers from data collisions the most?
A. Star
B. Bus
C. Ring
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: B
29. Ring topology performance degrades when:
A. More stations added
B. Central hub fails
C. One station transmits
D. No token available
✔ Ans: A
30. Which topology offers equal transmission opportunities to all nodes?
A. Mesh
B. Star
C. Bus
D. Ring (due to token passing)
✔ Ans: D
⭐ SECTION 6 — CONNECTIVITY & REDUNDANCY
31. Which topology provides a backup path for every node?
A. Bus
B. Star
C. Ring
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: D
32. A topology suitable for mission-critical networks is:
A. Mesh
B. Bus
C. Tree
D. Ring
✔ Ans: A
33. In Ring topology, failure of one node affects:
A. None
B. All nodes
C. Neighboring nodes only
D. Hub only
✔ Ans: B
34. Redundant links exist in:
A. Bus
B. Ring
C. Star
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: D
⭐ SECTION 7 — CABLING & COST
35. Which topology requires the least cable length?
A. Bus
B. Star
C. Ring
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: A
36. Which topology requires the MOST cable length?
A. Mesh
B. Star
C. Ring
D. Tree
✔ Ans: A
37. Which topology requires a terminator?
A. Star
B. Bus
C. Tree
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 8 — REAL-WORLD NETWORK USAGE
38. WANs mostly use which topology?
A. Star
B. Mesh
C. Tree
D. Bus
✔ Ans: B
39. MAN networks commonly use:
A. Ring topology
B. Bus topology
C. Tree topology
D. Hybrid topology
✔ Ans: A
40. LANs mostly use:
A. Bus
B. Star
C. Ring
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 9
41. A company requires maximum fault tolerance. Which topology?
A. Ring
B. Star
C. Mesh
D. Bus
✔ Ans: C
42. A small office needs low cost and minimal wiring. Which topology?
A. Star
B. Mesh
C. Bus
D. Ring
✔ Ans: C
43. For real-time communication with no collisions, choose:
A. Bus
B. Ring
C. Mesh
D. Tree
✔ Ans: B
44. For connecting branch offices across a city, best topology:
A. Bus
B. Ring
C. Mesh
D. Star
✔ Ans: C
45. For university campus backbone:
A. Star
B. Bus
C. Tree
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: C
⭐ SECTION 10 — HYBRID & SPECIAL TOPOLOGIES
46. Physical Star + Logical Ring is used in:
A. Ethernet
B. Token Ring
C. FDDI
D. WiFi
✔ Ans: B
47. Which is NOT a topology?
A. Tree
B. Mesh
C. Hybrid
D. Bridge
✔ Ans: D
48. Multiple star networks connected together form a:
A. Ring
B. Bus
C. Tree
D. Mesh
✔ Ans: C
49. Wireless networks typically use:
A. Mesh
B. Star
C. Bus
D. Ring
✔ Ans: B
50. Internet backbone largely uses:
A. Star
B. Full Mesh
C. Bus
D. Ring
✔ Ans: B
⭐ SECTION 11 — VERY HIGH EXPECTED QUESTIONS
51. Ring topology uses:
A. Half-duplex communication
B. Full-duplex communication
C. Simplex
D. Depends on design
✔ Ans: B
52. Example of Hybrid topology:
A. ATM networks
B. Bank branch networks
C. Data centers
D. All of the above
✔ Ans: D
53. Mesh topology improves reliability by:
A. Using multiple paths
B. Reducing nodes
C. Using cables only
D. Centralized control
✔ Ans: A
54. Star topology reduces:
A. Traffic collisions
B. Cable cost
C. Redundancy
D. Reliability
✔ Ans: A
55. Tree topology fails when:
A. Leaf node fails
B. Root node fails
C. Branch node fails
D. Terminator fails
✔ Ans: B
