1. Basics of Quantum Computing
| Concept | Explanation (Simple) | Example / Analogy |
|---|---|---|
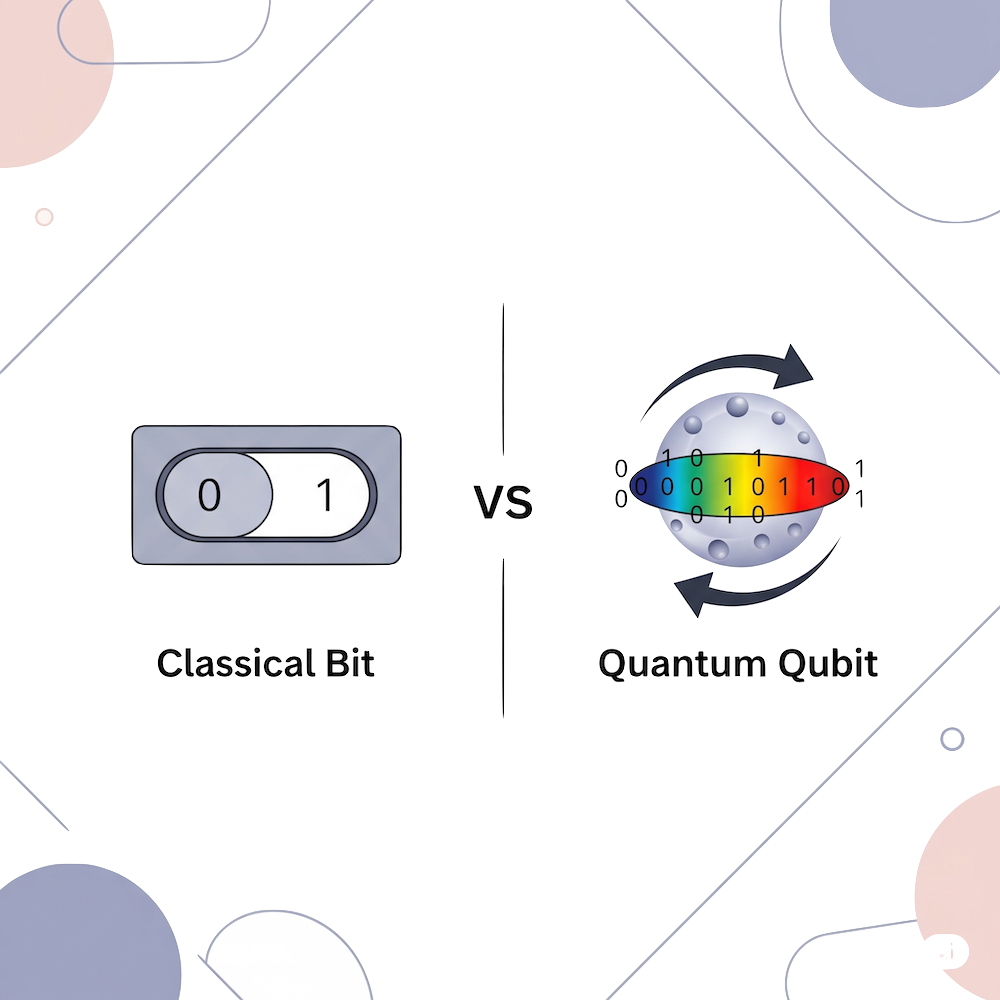
| Qubit | Quantum version of a bit. Can be 0, 1, or both (superposition) at the same time. | A special light switch that can be partly ON and partly OFF. |
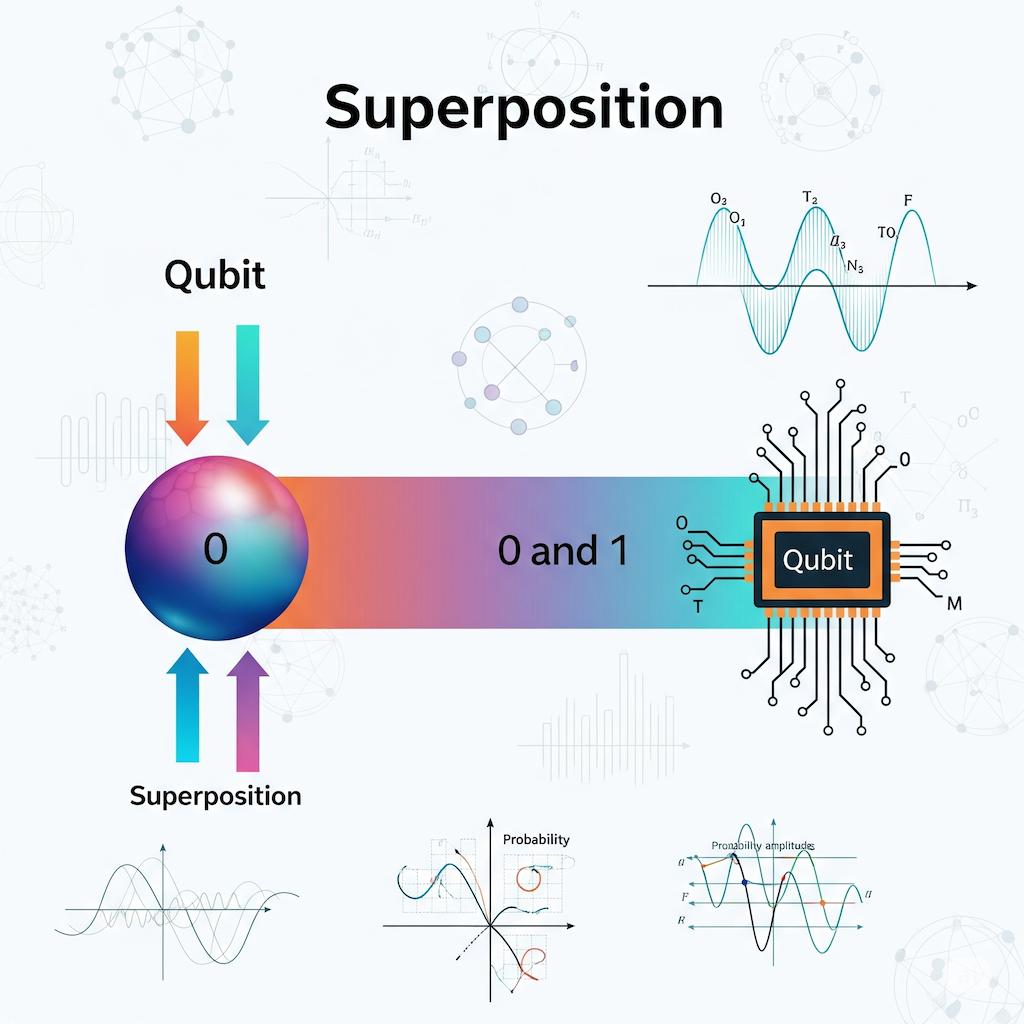
| Superposition | Ability of a qubit to be in multiple states at once until measured. | A coin spinning in the air (not yet heads or tails). |
| Entanglement | Two qubits are linked — changing one instantly affects the other, regardless of distance. | Two magic coins that always land opposite sides, even miles apart. |
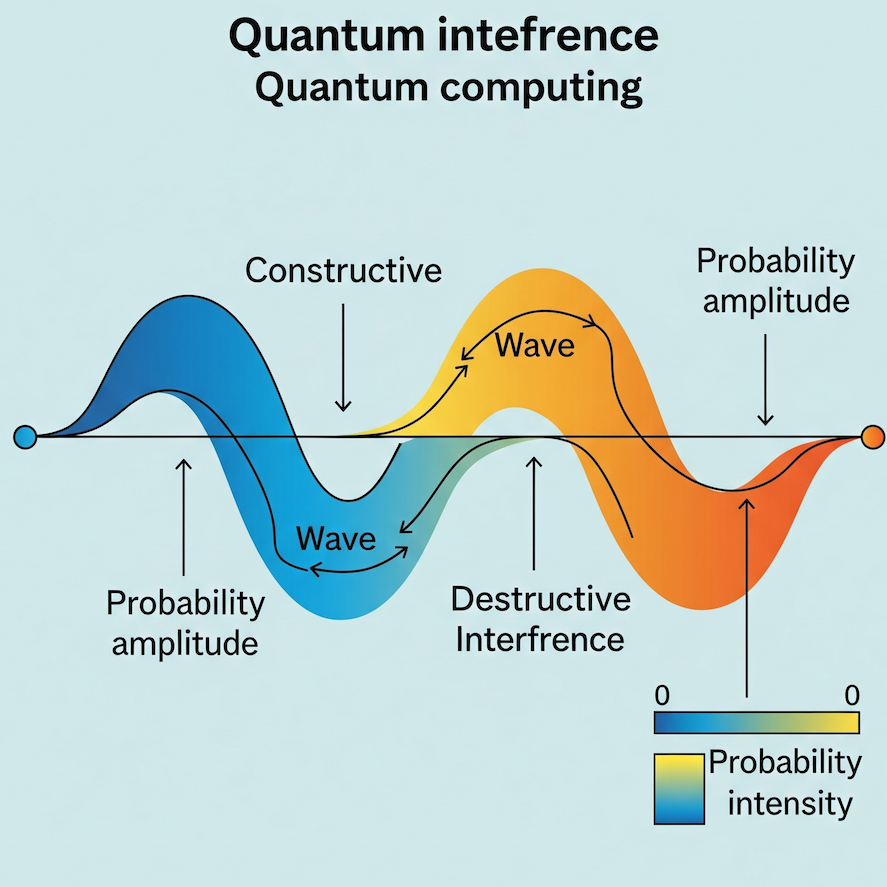
| Quantum Interference | Probability waves interact to amplify correct answers and cancel wrong ones. | Like sound waves syncing for louder sound or canceling noise. |
2. Quantum Gates
| Gate | Purpose | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Classical Gate | Flips a bit (0 → 1 or 1 → 0). | Light switch toggle. |
| Quantum Gate | Rotates qubits, creates superposition, builds entanglement, controls probabilities. | A precise dial adjusting ON/OFF levels. |
🔑 Key Idea: Quantum gates are the building blocks of quantum algorithms, just like logic gates in classical computers.
3. Quantum Algorithms
| Algorithm | Use | Key Point |
|---|---|---|
| Shor’s | Factorizes large numbers quickly. | Threatens RSA encryption. |
| Grover’s | Searches unsorted databases faster. | Speeds up search by √N factor. |
| Deutsch-Jozsa | Determines if a function is constant or balanced. | Needs only one check vs. many classical tries. |
4. Quantum Circuits
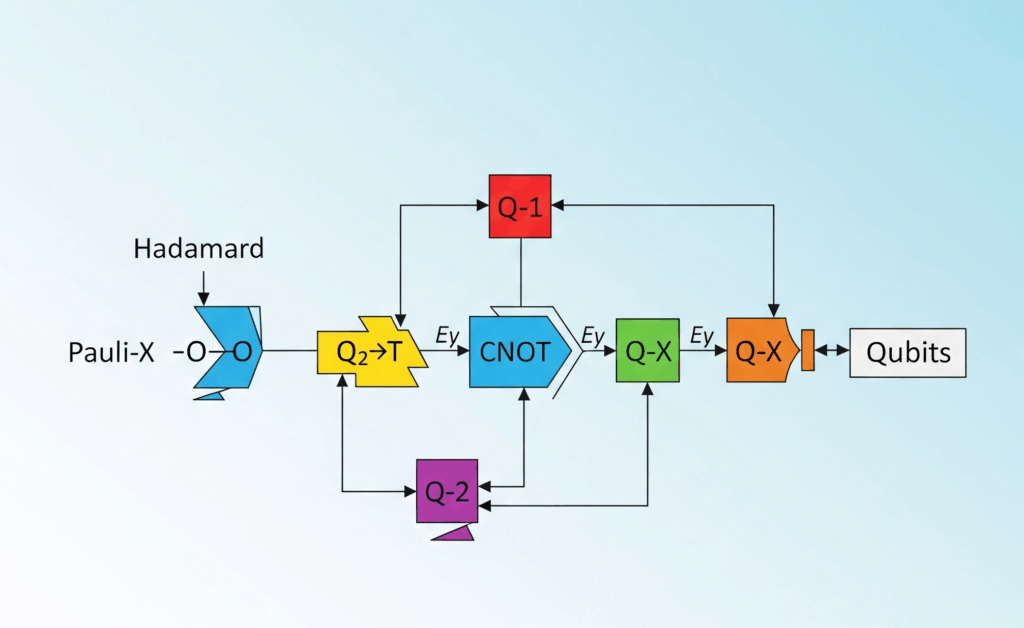
- Visual “blueprint” for quantum programs.
- Shows:
- Qubits (lines)
- Gates (boxes)
- Order (left → right)
- Measurement (where qubits collapse to 0 or 1)
Think of it as the recipe for a quantum computer’s operations.
5. Key Concepts
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Quantum Speedup | Solving some problems much faster than classical computers. |
| Quantum Decoherence | Loss of quantum information due to environment interference. |
| No-Cloning Theorem | Qubits can’t be perfectly copied. |
6. Quantum Computing Models
| Model | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Gate Model | Uses quantum gates for operations. | IBM Q. |
| Adiabatic QC | Slowly evolves system to optimal state. | Research-based models. |
| Quantum Annealing | Focused on optimization problems. | D-Wave systems. |
7. Quantum Hardware
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Superconducting Qubits | Use Josephson junctions; fast, scalable. | IBM, Google. |
| Trapped Ions | Use charged atoms in electromagnetic traps. | IonQ, Honeywell. |
| Photonic Qubits | Use light particles (photons). | PsiQuantum. |
| Topological Qubits | Uses quasiparticles; still experimental. | Microsoft’s research. |
8. Applications
| Field | Example Use |
|---|---|
| Cryptography | Breaking RSA, Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). |
| Machine Learning | Faster model training and optimization. |
| Optimization | Logistics, portfolio management. |
| Chemistry/Physics | Simulating molecules, material science. |
9. Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Hard to build large, stable quantum systems. |
| Error Correction | Qubits are fragile, easily disturbed by noise. |
| Physical Constraints | Requires extreme cooling and precise isolation. |
10. Leading Companies
- IBM Quantum – Cloud quantum computers.
- Google Quantum AI – Sycamore chip, achieved quantum supremacy.
- Rigetti, D-Wave, Honeywell, IonQ – Specialized quantum hardware and software platforms.
11. Important Terms & Acronyms
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Quantum Supremacy | Quantum computer solves a problem classical computers practically can’t. |
| Quantum Volume | Metric for a quantum computer’s computational capacity. |
| Bra-ket Notation | Mathematical notation for quantum states. |
| QEC | Quantum Error Correction. |
| QKD | Quantum Key Distribution (for secure comms). |
| CNOT | Controlled-NOT gate, essential for entanglement. |
12. Quick Recap Mnemonics
- Qubits: “Not just ON or OFF, but BOTH.”
- Superposition: “Fuzzy until you look.”
- Entanglement: “Magic link — spooky but useful.”
- Interference: “Amplify right answers, cancel wrong ones.”
- Quantum Algorithms: “Shor cracks, Grover searches, Deutsch tests.
MCQ
1. What is a qubit in quantum computing?
A. A classical binary digit
B. A unit of quantum information
C. A type of quantum hardware
D. A measure of quantum speed
Answer: B. A unit of quantum information
2. Which principle allows a qubit to exist in multiple states simultaneously?
A. Entanglement
B. Quantum Decoherence
C. Superposition
D. Quantum Interference
Answer: C. Superposition
3. What is quantum entanglement?
A. The interaction between photons and electrons
B. A phenomenon where two qubits are interdependent
C. The process of measuring qubits
D. The interference of quantum gates
Answer: B. A phenomenon where two qubits are interdependent
4. Which of the following is an advantage of quantum computing?
A. Unlimited memory storage
B. Breaking classical encryption systems efficiently
C. Zero hardware requirements
D. Elimination of computation errors
Answer: B. Breaking classical encryption systems efficiently
5. What is the role of a Hadamard gate in quantum computing?
A. Creates entanglement between qubits
B. Flips a qubit’s state
C. Puts a qubit into superposition
D. Measures the state of a qubit
Answer: C. Puts a qubit into superposition
6. Which algorithm is used for database search in quantum computing?
A. Shor’s Algorithm
B. Grover’s Algorithm
C. Dijkstra’s Algorithm
D. RSA Algorithm
Answer: B. Grover’s Algorithm
7. What is the main challenge faced by quantum computers?
A. High energy consumption
B. Quantum Decoherence
C. Limited processing speed
D. No practical applications
Answer: B. Quantum Decoherence
9. Which company developed the “Sycamore” quantum processor?
A. IBM
B. Microsoft
C. Google
D. Intel
Answer: C. Google
10. What does the No-Cloning Theorem state?
A. Quantum data cannot be erased
B. Quantum states cannot be exactly copied
C. Quantum computers can clone classical data
D. Only quantum gates can be cloned
Answer: B. Quantum states cannot be exactly copied
11. Which field is most likely to benefit from quantum computing?
A. Cryptography
B. Graphic Design
C. Marketing
D. Journalism
Answer: A. Cryptography
12. What is the significance of Shor’s Algorithm?
A. It speeds up searches in unsorted databases
B. It factors large numbers efficiently
C. It solves traveling salesman problems
D. It creates entanglement
Answer: B. It factors large numbers efficiently
13. Quantum computing is based on the principles of which branch of physics?
A. Classical Mechanics
B. Thermodynamics
C. Quantum Mechanics
D. Electromagnetism
Answer: C. Quantum Mechanics
14. What is Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) used for?
A. Enhancing classical encryption methods
B. Secure communication using quantum principles
C. Increasing memory in quantum computers
D. Faster data transmission
Answer: B. Secure communication using quantum principles
15. What does the CNOT gate do in quantum computing?
A. Creates a new qubit
B. Entangles two qubits
C. Erases quantum information
D. Measures the quantum state
Answer: B. Entangles two qubits
