1. What Are Joins?
SQL operations are used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column.
- Types of Joins:
- Inner Join
- Outer Join (Left, Right, Full)
- Cross Join
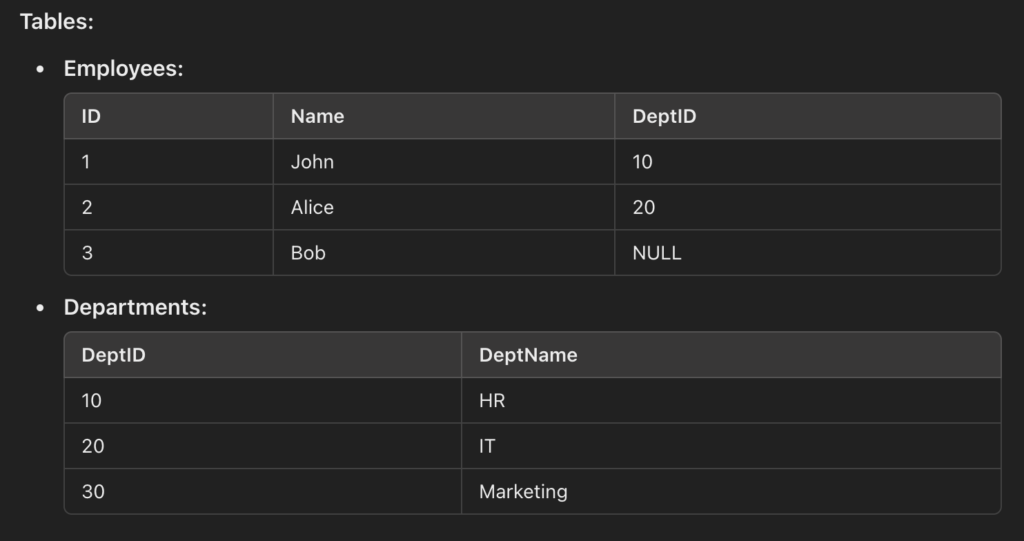
2. Inner Join (Matching Pairs Only)
Returns rows where there is a match in both tables based on the join condition. Keeps only rows where there is a match in both tables.
- Syntax:
SELECT columns FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
SELECT Employees.Name, Departments.DeptName
FROM Employees
INNER JOIN Departments ON Employees.DeptID = Departments.DeptID;
| Name | DeptName |
|---|---|
| John | HR |
| Alice | IT |
- “Show employees and their departments if they belong to a department.”
- Key Points:
- Excludes unmatched rows.
- Most commonly used type of join.
3. Outer Joins
a. Left Outer Join (Keep All From the Left)
Returns all rows from the left table, and the matching rows from the right table. Unmatched rows from the right table are filled with NULL.
- Syntax:
SELECT columns FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
SELECT Employees.Name, Departments.DeptName
FROM Employees
LEFT JOIN Departments ON Employees.DeptID = Departments.DeptID;
| Name | DeptName |
|---|---|
| John | HR |
| Alice | IT |
| Bob | NULL |
- Show all employees and their departments. If no department is assigned, show ‘NULL’.
- Key Point: Includes all rows from the left table, even if there is no match.
b. Right Outer Join (Keep All From the Right)
Returns all rows from the right table, and the matching rows from the left table. Unmatched rows from the left table are filled with NULL.
- Syntax:
SELECT columns FROM table1 RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
SELECT Employees.Name, Departments.DeptName
FROM Employees
RIGHT JOIN Departments ON Employees.DeptID = Departments.DeptID;
| Name | DeptName |
|---|---|
| John | HR |
| Alice | IT |
| NULL | Marketing |
- Show all departments and the employees in them. If no employees, show ‘NULL’.
- Key Point: Includes all rows from the right table, even if there is no match.
c. Full Outer Join (Everyone’s Included)
- Definition: Returns all rows when there is a match in either table, and fills unmatched rows with
NULL. - Syntax:
SELECT columns FROM table1 FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
SELECT Employees.Name, Departments.DeptName
FROM Employees
FULL OUTER JOIN Departments ON Employees.DeptID = Departments.DeptID;
| Name | DeptName |
|---|---|
| John | HR |
| Alice | IT |
| Bob | NULL |
| NULL | Marketing |
- Show all employees and all departments, even if they don’t match
- Key Point: Combines results of Left Join and Right Join.
4. Cross Join (Every Combination)
- Definition: Returns the Cartesian product of two tables (i.e., every row from the first table is paired with every row from the second table). Pair everyone in Group A with everyone in Group B.
- Syntax:
SELECT columns FROM table1 CROSS JOIN table2;
SELECT Employees.Name, Departments.DeptName
FROM Employees
CROSS JOIN Departments;
| Name | DeptName |
|---|---|
| John | HR |
| John | IT |
| John | Marketing |
| Alice | HR |
| Alice | IT |
| Alice | Marketing |
| Bob | HR |
| Bob | IT |
| Bob | Marketing |
- Pair every employee with every department (no real-world logic here).
- Key Points:
- No condition is required.
- Produces a large number of rows (rows in Table1 × rows in Table2).
Comparison Table
Quick Comparison
| Join Type | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Inner Join | Match and show rows that exist in both tables. |
| Left Join | All rows from the left table, match or no match. |
| Right Join | All rows from the right table, match or no match. |
| Full Outer Join | All rows from both tables, match or no match. |
| Cross Join | Every row from Table 1 pairs with every row in Table 2. |
| Join Type | Includes Unmatched Rows | Match Requirement | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inner Join | No | Only rows with matching values in both tables | Filtering matching data. |
| Left Outer Join | Yes (Left Table) | All rows from the left, matched or unmatched | Ensure all rows from the left table. |
| Right Outer Join | Yes (Right Table) | All rows from the right, matched or unmatched | Ensure all rows from the right table. |
| Full Outer Join | Yes (Both Tables) | All rows from both, matched or unmatched | Combine results of left and right join. |
| Cross Join | N/A | No condition; Cartesian product | Pairing all rows from both tables. |
Exam Tips
- Memorize the syntax and behavior of each join type.
- Understand the differences between Inner and Outer Joins (Left, Right, Full).
- Remember that Cross Join does not use a condition and produces a Cartesian product.
- Practice queries with real-world scenarios to solidify concepts.
✅ MCQs on Inner, Outer, Cross Joins (SQL Joins)
🔶 SECTION A — BASIC CONCEPTS
1. JOINs are used to:
A. Insert data
B. Update data
C. Combine rows from multiple tables
D. Create table
Answer: C
2. JOINs combine tables based on:
A. Primary Key only
B. Matching columns
C. NULL values
D. Same table always
Answer: B
3. A JOIN is performed using:
A. WHERE only
B. ON keyword
C. USING
D. Both B and C
Answer: D
🔶 SECTION B — INNER JOIN
4. INNER JOIN returns:
A. Only unmatched rows
B. Matched rows only
C. All rows
D. Only NULL rows
Answer: B
5. INNER JOIN works based on:
A. Equality condition
B. Primary key only
C. Unique key only
D. Default order of table
Answer: A
6. INNER JOIN between two tables gives:
A. Intersection
B. Union
C. Cartesian Product
D. Difference
Answer: A
7. INNER JOIN eliminates:
A. Duplicate rows
B. Unmatched rows
C. NULL values
D. All rows
Answer: B
8. Syntax of INNER JOIN:
A. SELECT … INNER JOIN table ON condition;
B. SELECT INNER table;
C. JOIN table USING;
D. SELECT table INNER;
Answer: A
9. INNER JOIN on Customer and Orders shows:
A. Only customers with orders
B. Only customers without orders
C. All customers
D. All orders
Answer: A
🔶 SECTION C — OUTER JOINS (LEFT, RIGHT, FULL)
⭐ LEFT OUTER JOIN
10. LEFT JOIN returns:
A. Only matches
B. All rows from left table + matched rows from right
C. All rows from right table only
D. Only unmatched rows
Answer: B
11. Unmatched right rows in LEFT JOIN appear as:
A. 0
B. NULL
C. EMPTY string
D. Ignored
Answer: B
12. LEFT JOIN focuses on preserving:
A. Right table
B. Left table
C. Both
D. None
Answer: B
⭐ RIGHT OUTER JOIN
13. RIGHT JOIN returns:
A. All rows from left
B. All rows from right
C. Only matched rows
D. NULL rows only
Answer: B
14. RIGHT JOIN is the opposite of:
A. FULL JOIN
B. LEFT JOIN
C. CROSS JOIN
D. INNER JOIN
Answer: B
15. Missing matches from left table are filled with:
A. 0
B. NULL
C. Blank
D. Duplicate
Answer: B
⭐ FULL OUTER JOIN
16. FULL OUTER JOIN returns:
A. Only matched rows
B. Only unmatched rows
C. All matched + unmatched rows from both tables
D. Only left table rows
Answer: C
17. FULL OUTER JOIN is equal to:
A. UNION of LEFT and RIGHT JOIN
B. INTERSECTION
C. MINUS
D. CROSS join
Answer: A
18. FULL JOIN shows NULL for:
A. Only left unmatched
B. Only right unmatched
C. Both sides unmatched
D. None
Answer: C
🔶 SECTION D — CROSS JOIN
19. CROSS JOIN returns:
A. Cartesian product
B. Intersection
C. Union
D. Unique rows only
Answer: A
20. If table A has 4 rows and table B has 3 rows, CROSS JOIN returns:
A. 4
B. 3
C. 7
D. 12
Answer: D (4 × 3)
21. CROSS JOIN requires:
A. ON condition
B. Matching key
C. No condition
D. Foreign key
Answer: C
22. CROSS JOIN is also known as:
A. Outer join
B. Full join
C. Cartesian join
D. Foreign join
Answer: C
🔶 SECTION E — SQL SYNTAX-BASED QUESTIONS
23. SELECT * FROM A INNER JOIN B ON A.id = B.id; returns:
A. Matched rows only
B. All rows
C. Left rows only
D. Right rows only
Answer: A
24. LEFT JOIN syntax:
A. SELECT … FROM A LEFT JOIN B ON condition;
B. SELECT LEFT …;
C. JOIN LEFT B;
D. SELECT * FROM JOINED A B;
Answer: A
25. FULL JOIN is supported in:
A. Oracle
B. PostgreSQL
C. SQL Server
D. All of the above
Answer: D
26. CROSS JOIN syntax:
A. SELECT * FROM A × B;
B. SELECT * FROM A CROSS JOIN B;
C. SELECT CROSS A B;
D. SELECT A,B CROSS;
Answer: B
🔶 SECTION F — INTERVIEW & EXAM FAVORITE TRICKY QUESTIONS
27. INNER JOIN with no matching rows returns:
A. All rows
B. NULL
C. No rows
D. All unmatched
Answer: C
28. LEFT JOIN with no matches in right table returns:
A. Only right rows
B. Only left rows (with NULLs on right)
C. No rows
D. Only matched rows
Answer: B
29. FULL JOIN with no matches on either side returns:
A. NULL on both sides
B. Matched rows only
C. Right rows only
D. Left rows only
Answer: A
30. CROSS JOIN without WHERE returns:
A. All matches
B. Tremendous number of rows
C. Only unique rows
D. Nothing
Answer: B
🔶 SECTION G — DIAGRAM/OUTPUT BASED QUESTIONS
Given:
Table A (Customers)
| ID | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Raj |
| 2 | Priya |
Table B (Orders)
| ID | OrderNo |
|---|---|
| 1 | O11 |
| 3 | O22 |
31. INNER JOIN on A.ID = B.ID gives rows:
A. (1, Raj, O11)
B. (2, Priya) only
C. (3, O22) only
D. All rows
Answer: A
32. LEFT JOIN results in:
| ID | Name | OrderNo |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raj | O11 |
| 2 | Priya | NULL |
Which join is this output from?
A. INNER JOIN
B. LEFT JOIN
C. RIGHT JOIN
D. CROSS JOIN
Answer: B
33. RIGHT JOIN results in:
| ID | Name | OrderNo |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raj | O11 |
| 3 | NULL | O22 |
This represents:
A. RIGHT JOIN
B. LEFT JOIN
C. FULL JOIN
D. CROSS JOIN
Answer: A
34. FULL OUTER JOIN result:
| ID | Name | OrderNo |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raj | O11 |
| 2 | Priya | NULL |
| 3 | NULL | O22 |
Which join gives this?
A. RIGHT JOIN
B. INNER JOIN
C. FULL OUTER JOIN
D. CROSS JOIN
Answer: C
35. CROSS JOIN result count is:
A rows × B rows =
A. 2
B. 3
C. 6
D. 5
Answer: C
🔶 SECTION H — BANKING SCENARIO QUESTIONS
36. To list all customers including those without accounts:
A. INNER JOIN
B. LEFT JOIN
C. CROSS JOIN
D. FULL JOIN
Answer: B
37. To list all accounts including those without customers:
A. RIGHT JOIN
B. LEFT JOIN
C. CROSS JOIN
D. FULL JOIN
Answer: A
38. To show all customers and all accounts:
A. LEFT JOIN
B. RIGHT JOIN
C. FULL OUTER JOIN
D. CROSS JOIN
Answer: C
39. To pair every product with every branch:
A. LEFT JOIN
B. CROSS JOIN
C. RIGHT JOIN
D. FULL JOIN
Answer: B
40. To display matched loan and branch records only:
A. INNER JOIN
B. LEFT JOIN
C. FULL JOIN
D. CROSS JOIN
Answer: A
🔶 SECTION I — COMPLEX & TRICKY (Internal Promotion Level)
41. FULL JOIN without WHERE removes:
A. Only nulls
B. No rows
C. Duplicates
D. Nothing
Answer: B
42. OUTER JOINs preserve:
A. Matches only
B. Unmatched rows also
C. Only NULL
D. Only equal rows
Answer: B
43. RIGHT OUTER JOIN preserves rows from:
A. Left
B. Right
C. Both
D. None
Answer: B
44. FULL OUTER JOIN is equivalent to:
A. LEFT JOIN + RIGHT JOIN
B. LEFT JOIN – INNER JOIN
C. CROSS JOIN
D. HAVING JOIN
Answer: A
45. CROSS JOIN result increases:
A. Linear
B. Exponential
C. Polynomial
D. Cartesian
Answer: D
🔶 SECTION J — TRUE / FALSE
46. INNER JOIN returns common records.
True
47. FULL JOIN returns unmatched records only.
False
48. LEFT JOIN always keeps left table rows.
True
49. CROSS JOIN requires ON condition.
False
50. RIGHT JOIN is rarely used compared to LEFT JOIN.
True
🔶 SECTION K — ADVANCED / BONUS 45–95 MCQs
51. CROSS JOIN + WHERE becomes:
A. INNER JOIN
B. LEFT JOIN
C. RIGHT JOIN
D. FULL JOIN
Answer: A
52. Which join can produce maximum number of rows?
A. INNER
B. LEFT
C. RIGHT
D. CROSS
Answer: D
53. OUTER JOIN that keeps everything from both tables:
A. LEFT
B. RIGHT
C. FULL
D. CROSS
Answer: C
54. A NULL appears in INNER JOIN when:
A. Never
B. Always
C. Sometimes
D. Only if full join
Answer: A
55. LEFT JOIN + unmatched rows shows NULL on:
A. Left table
B. Right table
C. Both
D. None
Answer: B
56. RIGHT JOIN + unmatched rows shows NULL on:
A. Left table
B. Right table
C. Both
D. None
Answer: A
57. FULL JOIN + no matches gives:
A. All NULL rows
B. No rows
C. Only left
D. Only right
Answer: A
58. INNER JOIN result is subset of:
A. LEFT JOIN
B. RIGHT JOIN
C. FULL JOIN
D. All of these
Answer: D
59. Most commonly used JOIN in SQL is:
A. CROSS
B. INNER
C. FULL
D. RIGHT
Answer: B
60. SQL JOIN type used in banking MIS reporting:
A. INNER
B. LEFT
C. FULL
D. All
Answer: D
